Dell 2850 Raid Driver For Mac
One of the owners of Velocity Tech Solutions and the CIO, AKA Best Geek Ever is looking of ways to help people get through the “SERVER HELL” of setting up raid. So often a tech will walk into a job where someone else set up the server and all is good in the world until it crashes.
They then enter “server hell” and since each machine is different, server hell can be a long hard road. For those having to set up a raid array on a Dell Poweredge 2850 Server, Kay Winchell has made it a bit easier. Read Below: RAID, or, is a term used to describe a method that can manage data among multiple on a server.
The main reason a Raid Array is used is for performance and, the benefits of which depend on the type of Raid chosen. The three most common types of Raid Arrays for servers are Raid 0, Raid 1, and Raid 5. Raid 0, which is also called, provides for higher performance and zero redundancy. The Raid controller writes data across all in the array and reads and writes to multiple disks at the same time.
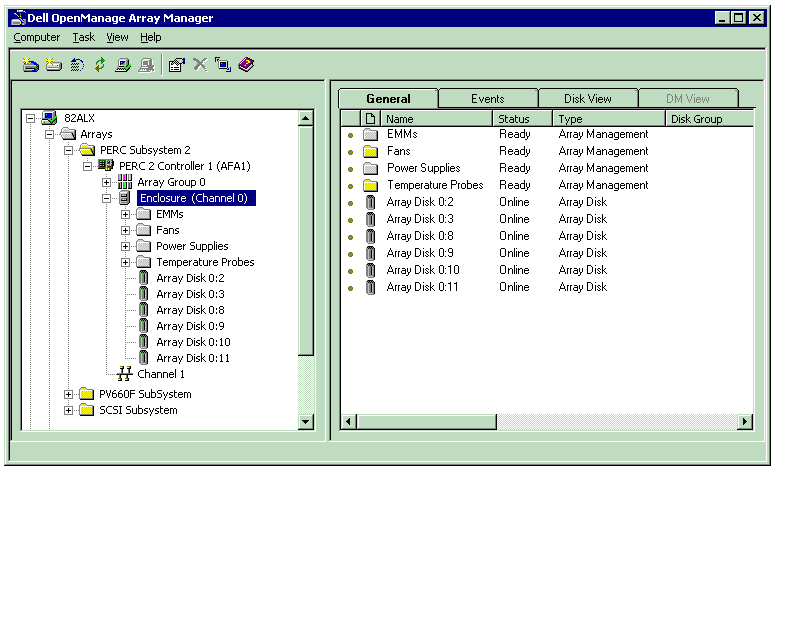
Speed is enhanced, however, if one hard drive in the array fails, all data is usually lost. Raid 1, which is also called Mirroring, provides for high redundancy, but zero increase in performance. Each hard drive is paired with another, one being a copy, or mirror, of the other. If one hard drive fails, the paired drive contains the same data. To set up Raid 1, the server must have at least two hard drives. Raid 5, which is also called Stripe Sets with Parity, has a mix of performance and redundancy benefits. Data is written to all of the drives in the array and data is written to all of the drives in the array as well.
The result is an increase in performance over while maintaining redundancy. If a hard drive in the array fails, a new drive can be added and the array repairs itself while the system continues to operate normally. For this reason, Raid 5 is the array of choice for most servers with three or more disks. Here are the instructions to set up a Raid Array for the. Please be aware that the instructions below are for setting up an array in a new server, not for adding drives to an array. Step 1: Power on the server.

The machine will go through POST at which time hardware components are identified and checked. Step 2: The server will now start to boot. A prompt will come up that says: Dell Poweredge Expandable RAID Controller Copyright © American Megatrends Inc. Press to run configuration utility.
Oct 27, 2014 - New GiD developer version has been released, and we are proud to announce that it is the first GiD 12.x version working native on Mac OS X. What's new from version 12.1.1d to 12.1.2d. Mac OS X: at the moment XCode does not support OpenMP, so disabling the Number of threads preferences for. Oct 27, 2014 - The Linux versions 12.0.2 and 12.1.1d x32 and x66 are also available now for. De: gidlist-bounces at listas.cimne.upc.edu [mailto:gidlist-bounces at. Version and the first Mac OS X GiD 12 version they will be available soon. God 12.1.1d also available for mac.
Step 3: After pressing, the Management Menu appears. The first item on the Management Menu is Easy Configuration. Select Easy Configuration. Step 4: A screen now appears with a listing of your hard drives. Press the SPACE bar for each drive you want to configure. Press Enter when finished selecting your drives. Step 5: Now you will choose your span, which is how many drives you want to configure into your array.
Use the spacebar to select your span. Press F10 when finished selecting your span. The reason you select a span is because multiple Raid Arrays can be set up within your drives. For instance, many administrators set up an array with the first two drives for the OS, with a second array for data. Step 6: A Screen now appears for Choose your Raid Level.
Dell Monitor Drivers For Mac
Depending on how many drives you have selected in your span, the system will offer you various options of Raid 0, 1, or 5. Arrow up or down and select your Raid level.
Dell Printer Drivers For Mac
Press Enter to accept. Step 7: At the prompt of Escape to Save Configuration, press yes. Your Raid Array is now configured. Anne Tarantino via Kay Winchell Velocity Tech Solutions.
Blog
- ✔ Initialize Drive For Mac
- ✔ Vw225n Driver For Mac
- ✔ Downloadhelper Firefox For Mac
- ✔ Manual For Ftm For Mac
- ✔ Descargar Gratis Video Downloadhelper For Mac
- ✔ Timeleft Deluxe Keygen For Mac
- ✔ Download Sharepod For Mac
- ✔ Art Inventory Software For Mac
- ✔ On-screen Softphone In Bolt For Mac
- ✔ Business Plan Template Apple Iwork Pages And Numbers For Mac
- ✔ Garmin Basecamp Software Download Free For Mac
- ✔ Mac Marshal: A Tool For Mac
- ✔ First Look: New Lucid Plug-ins For Photos For Mac
- ✔ Ms2137 Drivers For Mac
- ✔ Rim Offers More Details About Desktop Software For Mac
- ✔ Pdf Dvd Studio Pro 2 For Mac
- ✔ Descargar Apple Final Cut Pro X 10.4 For Mac